Table of Contents
- Introduction to PCB Backup Boards
- Evolution of Backup Board Functions
- PCB Drilling Methods
- Types of Backup Board Materials
- Factors Affecting Drilling Performance
- Research Findings on Backup Board Materials
- Spotlight: UV Coated White Backup Board
- Choosing the Right Backup Board
- Manufacturing and Quality Control
- Packaging and Shipping
- Environmental Considerations
- Industry Experience and Expertise
- Conclusion
1. Introduction to PCB Backup Boards
Back-up boards for printed circuit boards (PCBs) are an integral component in their production, providing drilling operations with support to allow precise holes with less damage to PCBs. Made of dense material such as high density paper or card stock, PCB back-up boards help ensure accuracy, efficiency and accuracy during drilling operations; their use serves to stabilize drilling process overall manufacturing quality while simultaneously supporting drilling operation accuracy and efficiency. With technology advancing so rapidly, choosing an ideal backup board to suit each PCB manufacturing quality level becomes ever more essential if optimal performance and long term product durability are ensured.
2. Evolution of Backup Board Functions
The role of PCB backup boards has evolved significantly since their inception. Initially designed purely for protection during the drilling process, these boards now provide a multitude of benefits that enhance both the efficiency of manufacturing and the quality of the final product.
Initial Purpose: Protection
Originally, backup boards were introduced as a safeguard against mechanical damage during drilling. They absorb vibrations and prevent the PCB from flexing, which can lead to misalignment of drill bits and result in inaccuracies. This basic function is crucial, particularly in applications requiring high precision, such as multilayer circuit boards.
Key Functions in Early PCB Manufacturing:
- Vibration Absorption:Reduces drill bit chatter, leading to smoother operations.
- Support Structure:Prevents flexing that could cause misalignment during drilling.
- Impact Resistance:Protects against potential physical damage from drilling operations.
Additional Benefits Discovered Through Research
As research progressed, manufacturers began to recognize that the material properties of backup boards could also influence drilling outcomes. Studies indicated that variations in hardness, density, and surface coatings could significantly affect:
Drilling Accuracy: Higher density materials can improve positional accuracy, resulting in better alignment of micro-holes and overall hole quality. For instance, using high-density wood fiber boards enhances the precision of holes as small as 0.15mm.
Drill Bit Longevity: Boards with superior surface hardness minimize drill bit wear, reducing the frequency of tool replacements and associated downtime. A study showed that using phenolic boards increased drill life by up to 30%.
Reduced Burr Formation: Certain materials help to minimize burrs on hole walls, leading to improved surface roughness and hole quality, essential for modern electronics. For example, UV-coated boards have been shown to provide a smoother finish, resulting in less post-drilling cleanup.
Case Study: High-Density Wood Fiber Board
A notable example is the adoption of high-density wood fiber boards (HDF) in PCB manufacturing. Research has shown that HDF significantly improves drilling performance for micro-aperture applications (e.g., FPCB micro-holes). Their inherent properties allow for better heat dissipation during the drilling process, which in turn enhances the overall quality of the drilled holes.
Advantages of HDF Boards:
- Enhanced Stability:High density provides excellent dimensional stability, crucial for maintaining precision in drilling operations.
- Improved Heat Management:The thermal properties of HDF help dissipate heat generated during drilling, preventing thermal damage to both the drill bit and the PCB.
- Versatility:Suitable for a variety of applications, including multilayer boards and flexible circuits.
Current Trends in Backup Board Functionality
In recent years, there has been a marked shift toward integrating smart technologies and eco-friendly materials in the production of backup boards. This includes:
Smart Materials: Some manufacturers are exploring the use of advanced composite materials that can adapt their properties based on the drilling conditions.
Eco-Friendly Options: With growing environmental concerns, the demand for sustainable materials has risen. Backup boards made from recycled or renewable resources are becoming more prevalent.
Summary
The evolution of backup board functions reflects a shift from simple protective measures to sophisticated tools that actively contribute to the quality and efficiency of PCB manufacturing. Understanding these advancements is crucial for manufacturers looking to optimize their production processes. The ongoing research and development in this field promise even more innovative solutions that will further enhance the performance of PCBs in various applications.
3. PCB Drilling Methods
Drilling is a critical process in the fabrication of printed circuit boards (PCBs), enabling the creation of pathways for electrical connections. There are several drilling methods utilized in the industry, each tailored for specific hole sizes and types. Understanding these methods is essential for selecting the appropriate backup board and ensuring optimal drilling performance.
Mechanical Drilling
Mechanical drilling is the most commonly used method for creating holes larger than 0.1 mm. This technique involves the use of rotating drill bits that penetrate the material, creating a physical hole.
Key Features of Mechanical Drilling:
- Versatile Bit Sizes:Drill bits can range from larger diameters for through-holes to smaller bits for more precise applications.
- Commonly Used Materials:High-density wood fiber boards (HDF), melamine backup boards, and phenolic boards are often employed as backup materials to support this process.
- Suitable Applications:Mechanical drilling is ideal for standard PCB applications, including multilayer circuit boards and standard-sized holes.
Advantages:
- High drilling speeds can be achieved, improving overall production efficiency.
- The method provides good hole quality with appropriate backing materials, leading to reduced burr formation and better hole positioning.
Disadvantages:
- It may lead to drill bit wear, necessitating frequent replacements.
- Heat generated during the drilling process can cause damage if not managed properly.
Laser Drilling
Laser drilling is a more advanced technique used primarily for creating holes smaller than 0.1 mm, often referred to as micro-holes. This method employs focused laser beams to vaporize the material, resulting in precise and clean holes.
Key Features of Laser Drilling:
- Precision:Capable of producing micro-apertures with exceptional accuracy, critical for modern electronic devices.
- No Mechanical Contact:Since the process is non-contact, it reduces the risk of damaging the PCB.
- Suitable Materials:UV-coated boards and other high-density composites can enhance performance, ensuring high positional accuracy and minimal thermal impact.
Advantages:
- The ability to create intricate designs and very small holes that traditional methods cannot achieve.
- Reduced mechanical stress on the PCB, preserving its structural integrity.
Disadvantages:
- Higher initial equipment costs compared to mechanical drilling methods.
- Limited to specific applications, as the high energy of lasers may not be suitable for all materials.
Comparison of Drilling Methods
| Feature | Mechanical Drilling | Laser Drilling |
| Hole Size Capability | > 0.1 mm | < 0.1 mm |
| Speed | High | Moderate |
| Material Interaction | Physical contact | Non-contact |
| Equipment Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Hole Quality | Good, with proper backing | Excellent, minimal burrs |
| Suitable Applications | Standard PCBs, multilayer | Micro-holes, flexible circuits |
Conclusion
Selecting the right drilling method is vital for ensuring the quality of the final PCB. Each method has its specific advantages and limitations, and the choice often depends on the required hole sizes, material types, and overall production goals. Furthermore, understanding the interaction between drilling techniques and backup board materials can lead to improved outcomes in both performance and efficiency.
4. Types of Backup Board Materials
The choice of backup board material is crucial in PCB manufacturing, directly influencing drilling performance, hole quality, and overall production efficiency. Various materials are used for backup boards, each offering distinct advantages and suitability for different applications. Below, we explore some of the most common backup board materials.
1. High-Density Wood Fiber Board (HDF)
High-density wood fiber boards are widely utilized for their excellent mechanical properties and stability.
Key Characteristics:
- Density:Typically ranges from 800 to 1,200 kg/m³, providing strong support during drilling.
- Dimensional Stability:HDF maintains its shape and size under various humidity conditions, reducing the risk of warping.
- Applications:Ideal for standard PCB and multilayer circuit board applications.
Advantages:
- Enhances drilling accuracy due to its rigidity.
- Minimizes drill bit wear and prolongs tool life.
2. UV Coated Boards
UV-coated boards have become increasingly popular in PCB manufacturing due to their protective properties and surface finish.
Key Characteristics:
- Surface Treatment:The UV coating provides a hard, smooth finish that resists scratches and chemical damage.
- Environmentally Friendly:Many UV coatings are designed to be eco-friendly, aligning with sustainability goals.
Applications: Often used in high-precision drilling operations where surface quality is paramount.
Advantages:
- Improves hole quality by minimizing burr formation and enhancing positional accuracy.
- Provides excellent moisture resistance, critical for electronic applications.
3. Phenolic Wood backup boards
Phenolic boards are known for their heat resistance and mechanical strength, making them suitable for demanding applications.
Key Characteristics:
- Thermal Stability:Excellent performance under high-temperature conditions, ideal for environments requiring durability.
- Low Moisture Absorption:Reduces the risk of deformation, especially in humid conditions.
Applications: Commonly used in applications involving multilayer circuits and high-frequency electronics.
Advantages:
- Reduces drill bit wear due to the toughness of the material.
- Offers superior surface hardness, leading to better hole quality.
4. Melamine Wood backup boards
Melamine boards are another option, providing a cost-effective solution for PCB manufacturing.
Key Characteristics:
- Affordability:Generally more economical than other materials, making it a popular choice for budget-conscious projects.
- Surface Finish:Melamine boards offer a smooth surface, aiding in the drilling process.
Applications: Often used for standard PCBs where high precision is not critical.
Advantages:
- Good dimensional stability, although less than HDF and phenolic boards.
- Suitable for a variety of applications, offering versatility.
5. Phenolic Paper backup boards
Phenolic paper backup boards combine the lightweight properties of paper with the durability of phenolic resin, offering a unique solution for backup boards.
Key Characteristics:
- Lightweight:Easier to handle and transport compared to traditional boards.
- Good Insulating Properties:Effective for electrical applications.
Applications: Useful for flexible circuits and situations where weight is a concern.
Advantages:
- Cost-effective and adaptable for various PCB configurations.
- Provides decent support during drilling without adding excessive weight.
Summary of Backup Board Materials
| Material | Density (kg/m³) | Key Advantages | Typical Applications |
| High-Density Wood Fiber | 800 – 1,200 | Excellent rigidity, minimizes wear | Standard and multilayer PCBs |
| UV Coated Boards | N/A | High surface quality, moisture resistance | High-precision drilling operations |
| Phenolic Wood backup boards | N/A | Thermal stability, low moisture absorption | High-frequency electronics |
| Melamine Wood backup boards | N/A | Cost-effective, smooth surface | Standard PCBs |
| Phenolic Paper backup boards | N/A | Lightweight, good insulation | Flexible circuits |
Conclusion
Choosing the right backup board material is essential for optimizing drilling performance and ensuring the quality of PCBs. Each material offers unique properties that cater to specific manufacturing needs, and understanding these differences is vital for manufacturers looking to enhance their production processes. By selecting the appropriate backup board, companies can achieve better drilling outcomes, minimize costs, and improve overall product quality.
5. Factors Affecting Drilling Performance
The performance of PCB drilling is influenced by several factors, including the choice of materials, drilling methods, and specific operational parameters. Understanding these elements is essential for optimizing the drilling process and achieving high-quality outcomes. Below, we explore the key factors that affect drilling performance.
1. Drill Bit Size and Speed
The size and speed of the drill bit are critical in determining the effectiveness of the drilling process.
Key Considerations:
- Bit Size:Larger drill bits are suitable for through-holes, while smaller bits are necessary for micro-holes. The choice of bit size directly affects the required backup board material.
- Drilling Speed:Faster drilling speeds can increase productivity but may also generate excessive heat, leading to potential damage to both the drill bit and the PCB. It’s crucial to find a balance between speed and quality.
Recommendations:
- Use appropriate cooling methods (e.g., lubrication) to manage heat during high-speed drilling.
- Adjust speeds according to the material being drilled; softer materials may allow for higher speeds, while harder materials may require slower speeds.
2. Positioning Effect of Backup Board
The stability and positioning provided by the backup board are vital for ensuring accuracy during drilling.
Key Points:
- Material Rigidity:High-density and rigid backup boards minimize flexing during drilling, helping to maintain drill bit alignment.
- Surface Flatness:A flat backup board surface ensures even support, which is essential for achieving consistent hole dimensions.
Impact on Performance:
- Inconsistent positioning can lead to misalignment, causing poor hole quality and increased burr formation.
- A well-chosen backup board significantly enhances the drilling accuracy of micro-apertures, particularly in multilayer circuit boards.
3. Drilling Depth
The depth of the holes being drilled impacts both the choice of materials and the drilling method.
Key Considerations:
- Deep Holes:For deeper holes, the heat generated can lead to thermal expansion and potential damage. Using materials with better thermal properties, such as phenolic boards, can help manage this.
- Hole Quality:Deeper holes may require adjustments in speed and bit type to ensure that the hole quality remains high and that the drill bit does not experience excessive wear.
Recommendations:
- Monitor drilling depth closely and adjust parameters as necessary to maintain quality.
- Consider using specialized drill bits designed for deeper holes to enhance performance and longevity.
4. Impact of Backup Board Hardness and Density
The hardness and density of the backup board material directly influence the drilling process.
Key Effects:
- Hardness:A harder backup board can reduce burr formation and enhance the quality of drilled holes. UV-coated boards are known for their excellent surface hardness.
- Density:Higher density materials provide better support, resulting in improved accuracy and reduced drill bit wear.
Performance Enhancement:
- Utilizing high-density wood fiber boards can significantly enhance the drilling of small holes by maintaining stability and reducing the risk of deformation during the process.
- Selecting the right hardness and density for the specific application can lead to notable improvements in hole quality and manufacturing efficiency.
5. Environmental Conditions
External factors such as humidity and temperature can also affect drilling performance.
Key Considerations:
- Humidity:High humidity can cause certain materials to swell or warp, impacting the stability of the backup board. Choosing materials with low moisture absorption, like phenolic boards, can mitigate this risk.
- Temperature:Elevated temperatures during drilling can affect both the material and the drill bit. Effective cooling strategies, such as lubrication or air cooling, should be employed to manage temperature.
Summary of Factors Affecting Drilling Performance
| Factor | Description | Impact on Performance |
| Drill Bit Size and Speed | Size affects hole quality; speed impacts heat generation | Balancing speed and quality is crucial |
| Backup Board Positioning | Stability ensures drill alignment | Reduces misalignment and enhances accuracy |
| Drilling Depth | Deeper holes require careful management of heat | Influences quality and bit wear |
| Board Hardness and Density | Hardness reduces burrs; density enhances support | Affects hole quality and longevity |
| Environmental Conditions | Humidity and temperature impact material stability | Proper material selection is essential |
Conclusion
Several interconnected factors affect the drilling performance in PCB manufacturing. By understanding these influences, manufacturers can make informed decisions regarding materials, drilling methods, and operational parameters to optimize outcomes. The careful selection of backup board materials, combined with effective drilling strategies, leads to improved accuracy, reduced costs, and higher-quality PCB products.
Would you like to continue to the next section?
6. Research Findings on Backup Board Materials
Recent research has highlighted the significant impact that backup board materials have on drilling performance, particularly in relation to hole sizes. Various studies have focused on the effects of different materials on both small and larger hole sizes, revealing insights that can guide manufacturers in their material selection.
Effects on Small Hole Sizes (0.15mm and 0.20mm)
For micro-holes, particularly those around 0.15mm to 0.20mm, the choice of backup board material is crucial.
Key Findings:
- High-Density Wood Fiber Boards (HDF):Research indicates that HDF enhances drilling accuracy for small apertures due to its rigidity and low thermal expansion characteristics. This results in better positional accuracy and reduced thermal deformation.
- UV-Coated Boards:The surface finish of UV-coated boards contributes to lower friction during drilling, reducing heat buildup and resulting in cleaner hole edges with fewer burrs.
Case Study: A study comparing drilling performance using HDF and standard MDF boards found that HDF significantly reduced misalignment in micro-holes, achieving a 20% improvement in accuracy.
Effects on Larger Hole Sizes (0.35mm)
For larger hole sizes, such as 0.35mm, the dynamics shift slightly, as the requirements for stability and heat management become paramount.
Key Findings:
- Phenolic Wood backup boards:These materials excel in maintaining structural integrity under high-temperature drilling conditions, ensuring consistent hole quality. The low moisture absorption of phenolic boards also helps prevent deformation during the drilling process.
- Melamine Boards:While generally less robust than phenolic boards, melamine backup boards can be effective for larger holes due to their affordability and decent performance in moderate conditions.
Research Conclusion: The study highlighted that using phenolic backup boards for larger hole sizes led to a 15% decrease in drill breakage rates, emphasizing the importance of material choice in achieving reliable outcomes.
Benefits of Increasing Backup Board Hardness and Density
Increased hardness and density of backup boards lead to numerous benefits in drilling operations:
- Improved Hole Quality:Higher hardness reduces burr formation and enhances surface finish.
- Extended Tool Life:Denser materials decrease drill bit wear, resulting in fewer replacements and downtime.
- Enhanced Dimensional Stability:More rigid materials maintain their shape better, resulting in more accurate drilling outcomes.
Summary of Research Findings
The choice of backup board material significantly influences drilling performance across different hole sizes. Both hardness and density play critical roles in achieving high-quality results, making research into material properties vital for manufacturers aiming for optimal drilling outcomes.
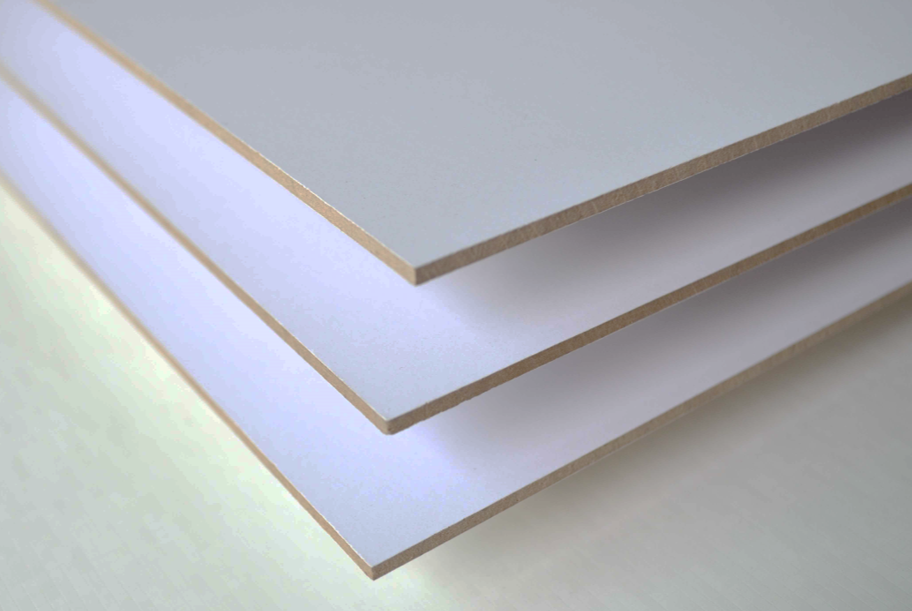
7. Spotlight: UV Coated White Backup Board
UV coated white backup boards have gained popularity in PCB manufacturing due to their exceptional properties and benefits. This section delves into the specifications, applications, and handling instructions associated with these advanced materials.
Product Specifications
Key Features:
- Surface Hardness:UV coating provides a high surface hardness, significantly reducing wear on drill bits.
- Moisture Resistance:The coating offers superior resistance to moisture, making it ideal for various environmental conditions.
- Color and Aesthetics:The white finish allows for better visibility during inspections and assembly processes.
| Specification | Value |
| Surface Hardness | High (specific values may vary) |
| Moisture Absorption | Low |
| Typical Thickness | 3mm to 6mm |
| Color | White |
Applications and Advantages
UV coated backup boards are particularly suited for high-precision drilling applications:
- Micro-Hole Drilling:The smooth surface minimizes friction and heat, essential for achieving high positional accuracy in micro-holes.
- Flexible Circuits:These boards are ideal for flexible PCBs, where bending and thermal stability are crucial.
- High-Temperature Environments:The thermal stability of UV coatings allows these boards to perform well under varying temperature conditions.
Advantages:
- Enhanced Drilling Accuracy:The superior surface finish helps maintain drill alignment, reducing misalignment in drilled holes.
- Reduced Burr Formation:The high hardness minimizes burrs, improving the overall quality of the finished PCB.
- Longevity and Durability:Increased durability leads to longer service life, providing cost savings over time.
Storage and Handling Instructions
Proper storage and handling of UV coated backup boards are essential to maintain their quality:
- Storage Conditions:Store in a cool, dry environment away from direct sunlight to prevent degradation of the UV coating.
- Handling Precautions:Avoid excessive force or impact, as this can damage the surface coating. Use gloves to prevent oils from hands from transferring onto the surface.
Conclusion
UV coated white backup boards represent a significant advancement in PCB manufacturing, offering numerous advantages in terms of performance and durability. Their specific properties make them particularly well-suited for high-precision applications, providing manufacturers with the tools necessary to achieve superior drilling results. As the demand for precision increases in the electronics industry, the role of advanced materials like UV coated boards will only continue to grow.
8. Choosing the Right Backup Board
Selecting the appropriate backup board is crucial for optimizing PCB drilling performance. Various factors should be considered to ensure that the chosen material meets the specific requirements of the manufacturing process. Below are key aspects to consider when choosing a backup board.
1. Application Requirements
Understanding the specific application is the first step in selecting the right backup board.
- Hole Size:Determine the range of hole sizes needed (micro-holes vs. larger apertures) as this will dictate the material’s rigidity and thermal properties required.
- PCB Type:Consider whether the PCB is a standard multilayer board or a flexible circuit, as different applications may necessitate different materials.
2. Material Properties
The physical and chemical properties of the backup board materials can significantly impact drilling performance.
- Density and Hardness:High-density and hard materials like phenolic boards are preferable for applications requiring precision and durability.
- Moisture Resistance:For environments with variable humidity, select materials with low moisture absorption to prevent warping.
3. Drilling Method Compatibility
Different drilling methods necessitate specific characteristics in backup boards.
- Mechanical Drilling:Look for materials that provide good stability and heat resistance, such as HDF or phenolic boards.
- Laser Drilling:Opt for UV-coated or other specialized boards that minimize heat and enhance hole quality.
4. Cost Considerations
While performance is critical, budget constraints also play a vital role in the decision-making process.
- Affordability vs. Performance:Weigh the costs of premium materials against potential gains in productivity and quality. While melamine boards are cost-effective, investing in higher-quality materials may yield better long-term results.
5. Manufacturer Reputation
Finally, consider the manufacturer’s experience and reputation in the industry.
- Quality Control Standards:Ensure the manufacturer adheres to stringent quality control measures, as this will directly affect the reliability and consistency of the backup boards.
- Support and Expertise:A reputable manufacturer will offer technical support and guidance in selecting the right materials for specific applications.
Summary of Selection Criteria
| Criteria | Considerations |
| Application Requirements | Hole size, PCB type |
| Material Properties | Density, hardness, moisture resistance |
| Drilling Method Compatibility | Compatibility with mechanical or laser drilling |
| Cost Considerations | Balancing performance with budget |
| Manufacturer Reputation | Quality control, support, and expertise |
Conclusion
Choosing the right backup board involves careful consideration of various factors that directly influence drilling performance and overall PCB quality. By aligning the material selection with specific application requirements and operational parameters, manufacturers can achieve optimal outcomes, enhancing productivity and reducing costs.
9. Manufacturing and Quality Control
The manufacturing process and quality control measures in the production of backup boards are crucial for ensuring that these materials meet the demanding standards of PCB manufacturing. This section outlines the key steps involved in the manufacturing process, as well as the quality control measures that are typically implemented.
1. Raw Material Selection
The first step in manufacturing backup boards involves selecting high-quality raw materials. The properties of the selected materials directly impact the performance of the finished product.
- Wood Fiber Sources:For HDF, ensure that the wood fibers are sourced sustainably and meet industry standards for quality.
- Resin Quality:The type and quality of the resin used in phenolic and melamine boards are critical for durability and moisture resistance.
2. Manufacturing Process Overview
The manufacturing process for backup boards typically involves several key steps:
- Preparation of Raw Materials:Wood fibers are processed and treated to enhance their properties before being combined with resin.
- Forming the Board:The prepared materials are compressed and heated to form the board. This step is critical for ensuring that the boards achieve the desired density and hardness.
- Finishing Treatments:Boards may undergo additional treatments, such as UV coating, to improve surface properties and enhance performance during drilling.
3. Quality Control Measures
Quality control is essential at every stage of the manufacturing process to ensure that the final product meets specifications.
- In-Process Testing:Regular checks during manufacturing for density, hardness, and moisture content help maintain quality standards.
- Final Inspection:Each batch of backup boards undergoes a final inspection to verify that they meet dimensional stability and surface finish requirements.
- Certification and Standards:Adherence to industry standards (e.g., IPC, ISO) is critical for ensuring the reliability and safety of backup boards in PCB applications.
4. Continuous Improvement
Manufacturers often implement continuous improvement practices to enhance production efficiency and product quality.
- Feedback Loops:Collecting feedback from end-users helps identify areas for improvement in both materials and processes.
- Research and Development:Investing in R&D allows manufacturers to explore new materials and technologies that can further enhance the performance of backup boards.
Summary of Manufacturing and Quality Control
| Step | Description |
| Raw Material Selection | Choosing high-quality, sustainable materials |
| Manufacturing Process | Compression, heating, and forming of boards |
| Quality Control Measures | In-process testing and final inspection |
| Continuous Improvement | Feedback loops and R&D investments |
Conclusion
The manufacturing and quality control processes for backup boards are vital for ensuring that these materials meet the high standards required for PCB manufacturing. By focusing on quality at every stage—from raw material selection to final inspection—manufacturers can produce reliable and effective backup boards that enhance drilling performance and overall PCB quality.
Would you like to proceed to the next section?
10. Packaging and Shipping
Proper packaging and shipping of backup boards are essential to maintaining their quality and ensuring they arrive in optimal condition for use in PCB manufacturing. This section discusses standard packaging methods and important shipping considerations.
1. Standard Packaging Methods
Backup boards require protective packaging to prevent damage during transit and handling.
- Protective Wrapping:Boards are typically wrapped in protective materials, such as bubble wrap or foam, to cushion them against impacts.
- Carton Boxes:Use sturdy, moisture-resistant cartons for shipping. These should be appropriately sized to prevent movement within the box.
- Palletizing:For bulk shipments, backup boards are often stacked on pallets to facilitate easier handling and loading. Proper palletizing helps prevent warping or bending during transport.
Example Packaging Procedure:
- Individual Wrapping:Each board is individually wrapped in protective material.
- Boxing:Wrapped boards are placed in moisture-resistant boxes.
- Labeling:Each box is clearly labeled with handling instructions and content descriptions.
- Palletizing (if necessary):Boxes are stacked on pallets and secured with shrink wrap.
2. Shipping Considerations
Shipping backup boards involves several key factors to ensure safe and efficient delivery.
- Humidity Control:Maintain stable humidity levels during shipping, as extreme moisture can affect the integrity of the boards. Use desiccants in shipping containers if necessary.
- Temperature Regulation:Protect boards from extreme temperatures, which can cause expansion or contraction, leading to warping or damage.
- Transportation Method:Choose transportation methods that minimize transit time and reduce handling. Air freight is typically faster, while sea freight is more economical for bulk shipments.
3. Documentation and Compliance
Ensure that all necessary documentation accompanies shipments to facilitate customs clearance and compliance with regulations.
- Shipping Documents:Include invoices, packing lists, and shipping labels with each shipment.
- Compliance Certifications:Provide any necessary quality certifications (e.g., ISO, IPC) required by the receiving company.
Summary of Packaging and Shipping
| Aspect | Description |
| Protective Wrapping | Use of bubble wrap or foam |
| Packaging Materials | Sturdy, moisture-resistant cartons |
| Palletizing | Stack boards on pallets for bulk shipments |
| Humidity Control | Maintain stable humidity levels |
| Temperature Regulation | Protect from extreme temperatures |
| Documentation | Include shipping documents and compliance certifications |
Conclusion
Effective packaging and shipping of backup boards are vital to preserving their quality and ensuring they perform as intended in PCB manufacturing. By implementing standardized procedures and considering environmental factors during transit, manufacturers can enhance customer satisfaction and reduce the risk of product damage.
11. Environmental Considerations
As the electronics industry continues to grow, so does the need for environmentally responsible practices in PCB manufacturing, including the selection and disposal of backup boards. This section examines eco-friendly options and waste disposal considerations.
1. Eco-Friendly Options
Many manufacturers are increasingly focused on sustainability, leading to the development of eco-friendly backup board materials.
- Recycled Materials:Some backup boards are made from recycled wood fibers or other sustainable sources, reducing the environmental impact of manufacturing.
- Low Formaldehyde Emission:Selecting boards with low formaldehyde emissions aligns with environmental regulations and promotes healthier working conditions.
- Biodegradable Materials:Innovations in biodegradable composites are emerging, providing options that reduce waste in landfills.
Benefits of Eco-Friendly Options:
- Regulatory Compliance:Meeting environmental regulations can enhance a manufacturer’s reputation and marketability.
- Consumer Demand:Many customers are seeking environmentally friendly products, making these options commercially viable.
2. Waste Disposal
Proper waste disposal methods are crucial for minimizing environmental impact.
- Recycling Programs:Manufacturers should implement recycling programs for scrap materials, ensuring that waste is repurposed rather than sent to landfills.
- Hazardous Waste Management:For boards treated with chemicals, proper hazardous waste disposal protocols must be followed to comply with local regulations.
- Education and Training:Provide training for employees on proper waste disposal methods to foster a culture of environmental responsibility.
3. Life Cycle Assessment
Conducting a life cycle assessment (LCA) can help manufacturers evaluate the environmental impact of their backup boards from production to disposal.
- Raw Material Extraction:Assess the environmental impact of sourcing raw materials.
- Manufacturing Processes:Evaluate energy consumption and emissions during production.
- End-of-Life Management:Consider options for recycling and disposal at the end of the product’s life cycle.
Summary of Environmental Considerations
| Consideration | Description |
| Eco-Friendly Options | Use of recycled, low-emission, or biodegradable materials |
| Waste Disposal | Implementation of recycling programs and proper hazardous waste management |
| Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) | Evaluate environmental impact from production to disposal |
Conclusion
Environmental considerations in the production and disposal of backup boards are increasingly important in today’s manufacturing landscape. By adopting eco-friendly practices and effective waste management strategies, manufacturers can not only comply with regulations but also contribute positively to the environment while meeting consumer demand for sustainable products.
Would you like to proceed to the next section?
12. Industry Experience and Expertise
In the rapidly evolving field of PCB manufacturing, the experience and expertise of manufacturers play a crucial role in delivering high-quality backup boards. As the industry faces increasing demands for precision, sustainability, and innovation, the knowledge and skills of manufacturers become vital for meeting these challenges.
1. Importance of Manufacturer Experience
Experience in the industry brings several advantages:
Technical Knowledge: Established manufacturers possess a deep understanding of material properties and their impacts on drilling performance. This expertise allows for the selection of optimal materials tailored to specific applications.
Process Optimization: Experienced manufacturers are adept at refining production processes to enhance efficiency and reduce waste. They can implement best practices that result in better quality control and consistency.
Problem Solving: With years of experience, manufacturers are more equipped to troubleshoot issues that arise during production or drilling, ensuring timely resolutions that prevent costly delays.
2. Advancements in Backup Board Technology
The PCB industry is witnessing significant advancements in backup board technology, driven by both research and practical experience.
Material Innovations: Ongoing research into composite materials and eco-friendly alternatives is leading to the development of backup boards that offer superior performance while reducing environmental impact.
Smart Technologies: Some manufacturers are exploring the integration of smart materials that can adapt to changing conditions during the drilling process, improving efficiency and accuracy.
Automation and AI: The incorporation of automated systems and artificial intelligence in manufacturing processes allows for precise control and monitoring, leading to higher quality outputs and reduced labor costs.
3. Industry Collaboration
Collaboration between manufacturers, research institutions, and industry organizations is essential for advancing technology and best practices.
Joint Research Initiatives: Collaborative research projects can drive innovation in materials and processes, benefiting the entire industry.
Training and Development: Partnerships with educational institutions can provide training programs that keep employees updated on the latest technologies and industry standards.
Summary of Industry Experience and Expertise
| Aspect | Importance |
| Manufacturer Experience | Technical knowledge, process optimization, problem-solving |
| Advancements in Technology | Material innovations, smart technologies, automation |
| Industry Collaboration | Joint research, training and development |
Conclusion
The experience and expertise of manufacturers in the PCB industry are crucial for navigating the challenges of modern production. By focusing on innovation and collaboration, manufacturers can enhance their capabilities, leading to improved quality and performance in backup boards and other components.
13. Conclusion
In summary, understanding PCB backup boards is essential for anyone involved in the manufacturing and assembly of printed circuit boards. From their fundamental role in providing support during drilling to the complexities of material selection and the impact of environmental considerations, every aspect plays a significant role in the final product quality.
Key Takeaways:
Material Selection: The choice of backup board materials—such as high-density wood fiber boards, UV-coated boards, and phenolic backup boards—directly influences drilling performance, accuracy, and overall PCB quality.
Drilling Methods: Knowledge of different drilling methods, including mechanical and laser drilling, is crucial for determining the appropriate backup board and achieving optimal results.
Quality Control: Robust manufacturing processes and stringent quality control measures are vital for ensuring that backup boards meet the high standards required in the industry.
Environmental Responsibility: As sustainability becomes a priority, eco-friendly options and effective waste disposal methods are essential for minimizing the environmental impact of PCB manufacturing.
Experience and Innovation: Industry experience and advancements in technology are key drivers of progress in backup board production, helping manufacturers adapt to evolving demands and improve efficiency.
Future Trends
As the electronics industry continues to grow, the need for high-quality, precise, and environmentally friendly PCB solutions will only increase. Manufacturers that invest in research, embrace new technologies, and focus on quality will be well-positioned to meet the challenges of the future.
By considering all these factors, stakeholders in the PCB industry can make informed decisions that enhance production processes and lead to superior product outcomes.
Thank you for exploring this comprehensive guide on PCB backup boards! If you have any further questions or need additional information, feel free to ask.