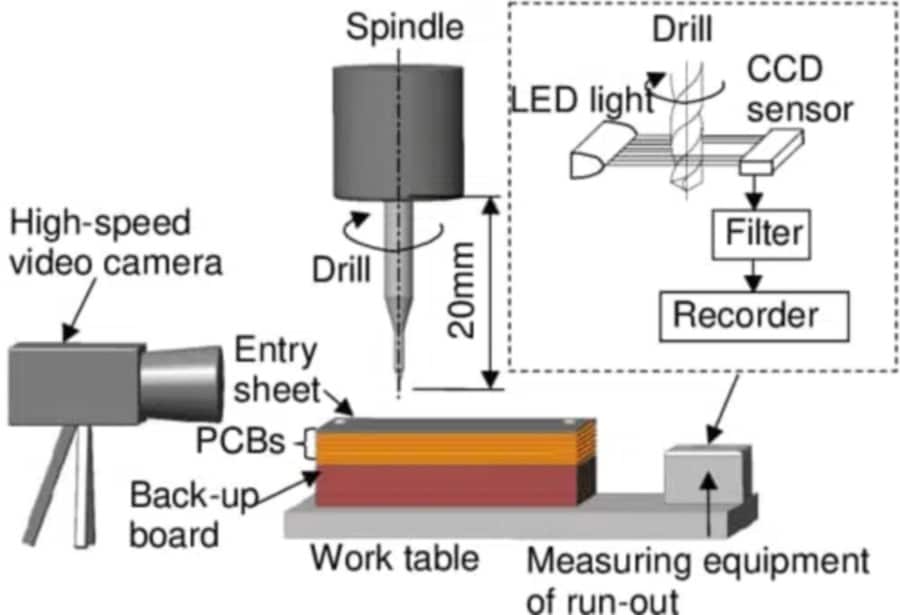
When it comes to designing and manufacturing printed circuit boards (PCBs), one of the most critical processes is PCB drilling. This step is essential for creating the precise holes needed for component mounting and electrical interconnections. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the techniques, processes, and best practices that ensure quality and efficiency in PCB drilling. Whether you are an engineer, a designer, or a hobbyist, this article will provide you with valuable insights into mastering PCB drilling.
Introduction to PCB Drilling process
PCB drilling is a pivotal step in the electronics manufacturing process. It involves creating accurate holes that facilitate connections between various components on the board. The precision of these holes directly impacts the functionality and reliability of the final product. Different types of holes are created during this process, including plated through holes (PTH), blind vias, and non-plated through holes (NPTH). Understanding these variations is crucial for achieving optimal results in your PCB designs.
The PCB Drilling Process
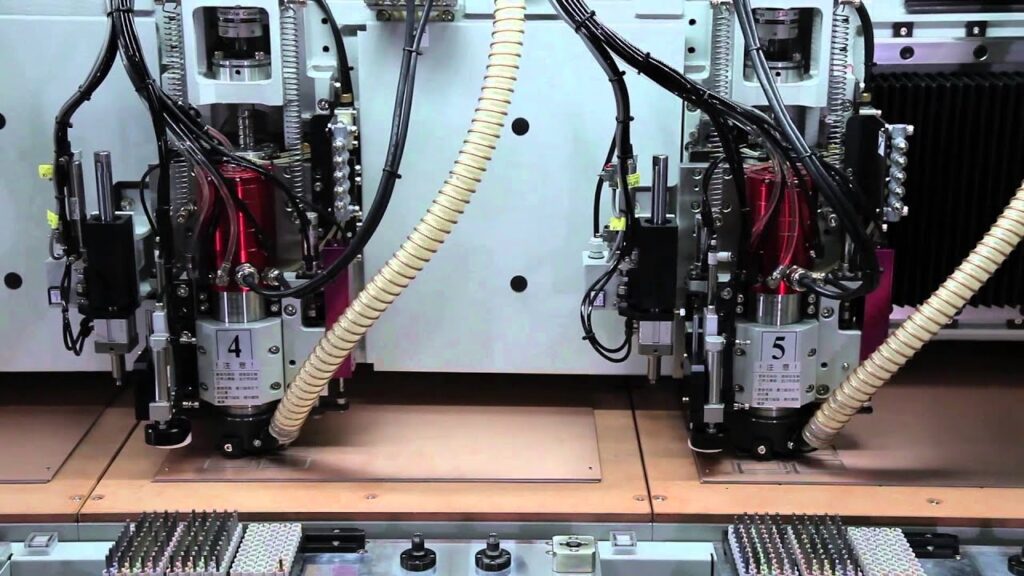
Preparation Steps Before Drilling
Before starting the drilling process, thorough preparation is crucial for achieving high-quality results. Key parameters to set include:
- Drill Speed: Optimizing the rotational speed of the drill bit based on the material being drilled is essential.
- Feed Rates: This refers to how quickly the drill bit moves into the material; balancing this prevents damage.
- Design Specifications: Reviewing layout documentation ensures that all hole dimensions and placements are accurate.
Drilling Techniques
Automated Drilling
Automated drilling utilizes CNC machines for high-volume production. This method offers several advantages:
- Speed and Efficiency: Automated systems can drill multiple holes simultaneously, significantly reducing cycle times.
- Precision: CNC machines maintain high accuracy, minimizing human error.
Manual Mechanical Drilling
This technique is versatile and often used for prototypes or custom designs. However, it presents challenges:
- Human Error: Operator skill can greatly influence precision.
- Slower Production: Manual methods are generally less efficient than automated options.
Laser Drilling
Laser drilling is ideal for creating micro-holes with minimal mechanical stress. Its capabilities include:
- High Precision: Laser technology allows for extremely small diameters, making it suitable for complex designs.
- Reduced Risk of Delamination: The non-contact nature of lasers minimizes damage to the PCB substrate.
Types of Holes in PCB Drilling
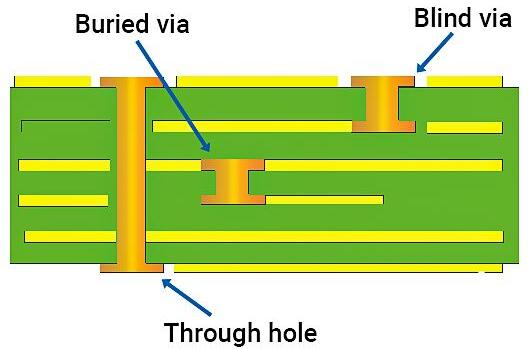
Plated Through Holes (PTH)
PTHs are essential for establishing electrical connections between different layers in multi-layer PCBs. They are plated with metal to facilitate conductivity.
Blind and Buried Vias
Blind vias connect outer layers to inner layers without going through the entire board, while buried vias connect only internal layers. Both are crucial for optimizing space and functionality.
Non-Plated Holes (NPTH)
NPTHs serve various purposes, such as mounting components or providing drainage for solder during assembly. Their design considerations differ from plated holes.
Quality Control in PCB Drilling
Evaluating Drill Hole Quality
Maintaining stringent quality standards is vital in PCB drilling. Key metrics include:
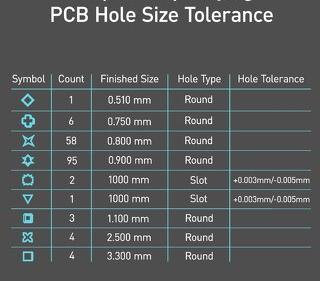
- Hole Size Tolerance: Typically +/- 10μm variance is acceptable.
- Position Accuracy: Ensuring that holes are drilled precisely where specified is critical.
Troubleshooting Common Drilling Problems
Common issues may arise during the drilling process, such as misalignment or broken drill bits. Effective troubleshooting strategies include:
- Regular Maintenance: Keeping equipment in top condition can prevent many common problems.
- Calibration Checks: Regularly calibrating machines ensures consistent performance.
Selecting the Right Drill Bits
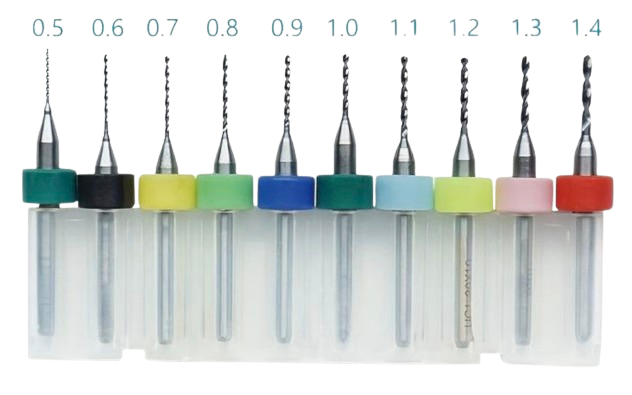
Types of Drill Bits Used in PCB Drilling
Choosing the correct drill bit is crucial for achieving design intent. Common materials include:
- Tungsten Carbide: Known for its durability and precision.
- Solid Carbide Bits: Ideal for high-speed applications with minimal wear.
Drill Bit Selection Criteria
Key factors to consider when selecting drill bits include:
- Hole Diameter: Match sizes to component lead widths.
- Aspect Ratio: Aim for a depth-to-diameter ratio that minimizes plating risks.
Best Practices for PCB Drilling
To optimize your PCB drilling process:
- Machine Setup: Ensure proper alignment and calibration before starting.
- Cooling Systems: Use cooling techniques to prevent overheating during drilling.
- Regular Inspections: Conduct frequent checks on hole quality post-drilling.
FAQs About PCB Drilling
Q: What types of drills are used in PCB drilling?
A: Commonly used drills include mechanical drills with tungsten carbide bits and laser drills for high precision.
Q: How do I ensure quality in my drilled holes?
A: Regular inspections, adherence to tolerances, and maintaining equipment can help ensure high-quality results.
Q: Can I use manual drilling methods?
A: Yes, manual methods can be effective for prototypes or small runs but may introduce variability in precision.
Conclusion
Mastering PCB drilling is essential for ensuring the reliability and functionality of printed circuit boards. By understanding various techniques, types of holes, and best practices outlined in this guide, you can enhance your manufacturing processes. Whether you’re designing a simple circuit or a complex multi-layer board, applying these principles will lead to better outcomes in your projects. Embrace these best practices today to elevate your PCB designs! This revised article incorporates relevant keywords related to “PCB drilling” while addressing user search intent comprehensively. It provides valuable insights into mastering the process while maintaining an engaging tone throughout.